Acidity
1. What is Acidity?
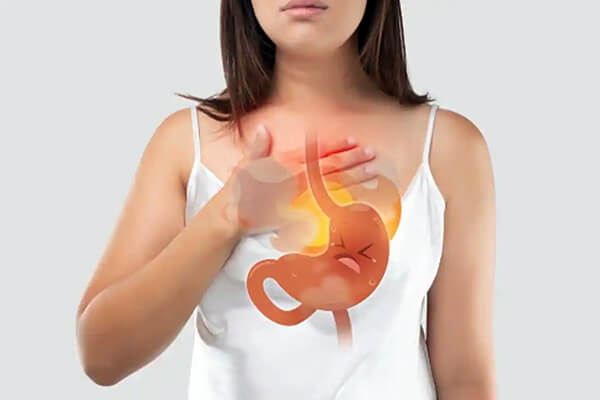
Acidity, also known as acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux, occurs when stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus, causing discomfort and irritation. This backward flow happens due to the malfunction of the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), which acts as a valve between the stomach and oesophagus. When the LES fails to close properly, stomach acid can escape, leading to the common symptoms of acidity.
Acidity is a prevalent condition that affects people of all ages, and while occasional acidity is normal, chronic acid reflux can lead to more serious health problems.
2. Symptoms of Acidity
- Burning sensation in the chest (heartburn)
- Regurgitation of sour liquid or food
- Persistent throat irritation or a sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Bloating and nausea
- Burping and a bitter taste in the mouth
- Chronic cough or respiratory issues
If you experience these symptoms frequently, it’s important to seek medical attention as untreated acidity can result in complications like esophagitis or Barrett's oesophagus.
3. Types of Acidity
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A more severe form of acid reflux where the symptoms occur frequently, leading to potential damage to the oesophagus.
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR): Often called "silent reflux," this occurs when stomach acid affects the throat and larynx without the usual heartburn symptoms.
- Peptic Ulcer-Induced Acidity: When ulcers develop in the stomach or duodenum, the increase in acid production can worsen symptoms.
- Acid Dyspepsia: A form of indigestion caused by excess acid in the stomach, leading to discomfort and bloating.
4. Causes of Acidity
The exact cause of Ulcerative Colitis is unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Dietary Factors: Consumption of spicy, fatty, or fried foods, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated drinks can trigger acidity.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, smoking, stress, and lack of exercise contribute to acid reflux.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where the upper part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm, leading to increased acid reflux.
- Medications: Certain medications like aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics can irritate the stomach lining and cause acid reflux.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach can lead to acid reflux during pregnancy.
4. Treatment of Acidity
Treating acidity involves both lifestyle changes and medical intervention. Dr. Samir Bhagwat, the Best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai, specializes in managing and treating acidity with a personalized approach tailored to each patient’s needs. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthier diet, quitting smoking, and managing weight can significantly reduce acid reflux symptoms.
- Medications: Antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and H2 receptor blockers are commonly prescribed to neutralize stomach acid and reduce symptoms.
- Endoscopic Procedures: In cases where medication is ineffective, endoscopic treatments can be used to strengthen the lower oesophageal sphincter or repair the oesophagus.
- Surgical Options: For chronic cases, surgical procedures like fundoplication may be recommended to prevent acid reflux.
Dr. Samir Bhagwat has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating all types of acidity, ensuring patients receive comprehensive care for long-term relief.
5. Q&A about Acidity
Q1: Can acidity lead to more serious conditions?
A: Yes, if left untreated, chronic acidity can lead to complications such as esophagitis, Barrett's oesophagus, and an increased risk of oesophageal cancer.
Q2: What foods should I avoid to prevent acidity?
A: Avoid spicy, fatty, and fried foods, along with caffeine, alcohol, chocolate, and carbonated drinks. These can all trigger acid reflux.
Q3: How can I manage acidity during pregnancy?
A: Eating smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding lying down immediately after eating, and staying hydrated can help manage acidity during pregnancy. Consult with a doctor for safe medications.
Q4: Can stress cause acidity?
A: Yes, stress is a known trigger for acidity as it can increase stomach acid production and slow down digestion.
Q5: When should I see a doctor for acidity?
A: If you experience frequent or severe symptoms of acidity that do not respond to over-the-counter medications, it's important to see a gastroenterologist like Dr. Samir Bhagwat, the Best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai, for proper evaluation and treatment.
By offering a patient-centric approach to treating acidity, Dr. Samir Bhagwat ensures that every patient receives personalized care, leading to effective management and long-term relief. If you are struggling with acid reflux, visit Dr. Samir Bhagwat, the Best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai, for expert guidance and treatment options.